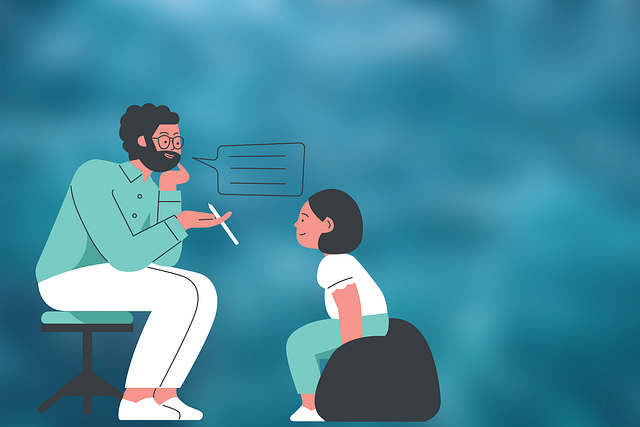
Depression in young children is a growing concern, but early intervention through therapy for young children can significantly improve outcomes. Recognizing signs as early as 3 or 4 years old is crucial. Therapists-clinicians guide both children and families through crisis intervention and tailored therapy sessions to teach stress reduction methods, fostering resilience and emotional well-being. A comprehensive approach integrates evidence-based practices into mental health policy advocacy, ensuring accessible resources for all children. Early detection prevents more severe depressive episodes later in life, emphasizing the importance of therapy for young children strategies for a healthier future.
Depression among young children is a growing concern, but with proactive strategies, it can be prevented. This article explores essential aspects of depression prevention, focusing on early intervention techniques tailored for young minds. We delve into the critical roles therapists and clinicians play in both treatment and prevention, offering valuable insights for professionals. Additionally, we provide practical tips for parents and caregivers to create supportive environments, fostering resilience and mental well-being in children. Discover how therapy for young children and guidance for therapists can make a significant impact on this pressing issue.
- Understanding Depression in Young Children: Early Intervention Strategies
- The Role of Therapists and Clinicians in Prevention and Treatment
- Creating a Supportive Environment: Tips for Parents and Caregivers
Understanding Depression in Young Children: Early Intervention Strategies

Depression among young children is a growing concern, but early intervention can significantly improve outcomes. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of depression in kids as young as 3 or 4 years old is crucial for effective therapy for young children. Children’s mental health professionals play a vital role in providing crisis intervention guidance to both children and their families. Through tailored therapy sessions, therapists-clinicians can help young minds navigate stress reduction methods, fostering resilience and emotional well-being.
A comprehensive approach involves not just individual therapy but also integrating evidence-based practices into the broader mental health policy analysis and advocacy landscape. By doing so, we ensure that resources and strategies for depression prevention are accessible to all children, regardless of their socio-economic backgrounds. Early detection and intervention have been shown to prevent more severe depressive episodes later in life, underscoring the importance of these strategies in shaping a healthier future for our youngest population.
The Role of Therapists and Clinicians in Prevention and Treatment

Therapists and clinicians play a pivotal role in both preventing and treating depression, especially in young children. Early intervention is crucial in addressing depressive symptoms before they escalate. Through therapy sessions, professionals can equip children with essential coping skills to manage stress and emotions effectively. This proactive approach not only prevents the onset of depression but also fosters resilience, enabling youngsters to navigate challenges with newfound strength.
For therapists and clinicians, specialized training in child psychology is vital to understand the nuances of childhood depression. By tailoring therapy sessions to cater to young minds, they can create a safe space for children to express their feelings, process traumatic experiences, and develop healthier emotional regulation strategies. This personalized approach complements medication (when necessary) and significantly contributes to the holistic Depression Prevention and Anxiety Relief for younger individuals.
Creating a Supportive Environment: Tips for Parents and Caregivers

Creating a supportive environment is a crucial aspect of depression prevention, especially when it comes to young children and their parents or caregivers. The home setting plays a significant role in shaping a child’s mental health and resilience. Parents and caregivers can foster a positive atmosphere by promoting open communication about emotions and providing a safe space for expression. This involves actively listening to the child’s concerns, validating their feelings, and teaching them healthy coping mechanisms. For instance, incorporating activities like Mindfulness Meditation can help children develop self-awareness and emotional regulation skills, which are essential tools in preventing depression.
Additionally, ensuring regular routines and structured environments can offer a sense of predictability and security. Therapists and clinicians working with families can guide parents in setting realistic expectations and promoting healthy habits. Regular check-ins for risk assessment can help identify early signs of distress, allowing for timely intervention through therapy for young children. By combining these strategies, parents and caregivers can effectively contribute to depression prevention while fostering a nurturing environment that supports the overall well-being of their children.
Depression prevention is a multifaceted approach that involves early intervention, tailored therapy for young children, and creating supportive environments. Therapists and clinicians play a crucial role in identifying signs early on and providing effective treatments. By implementing these strategies—including those aimed at parents and caregivers—we can foster resilience and promote mental well-being in young individuals, ensuring they receive the necessary support to thrive.